LoopBack 4 Offers Inclusion of Related Models
Originally published on strongloop.com
LoopBack 4 now offers a new feature: inclusion of related models! This addition not only simplifies querying data in LoopBack 4, but since we have similar features in LoopBack 3 it also closes one feature gap between LoopBack 3 as well. The idea is to use the inclusion resolver, which is a function that helps to query data over different relations, to achieve such simplifications for us.
Here is a simple use case of inclusion: a customer has many orders.
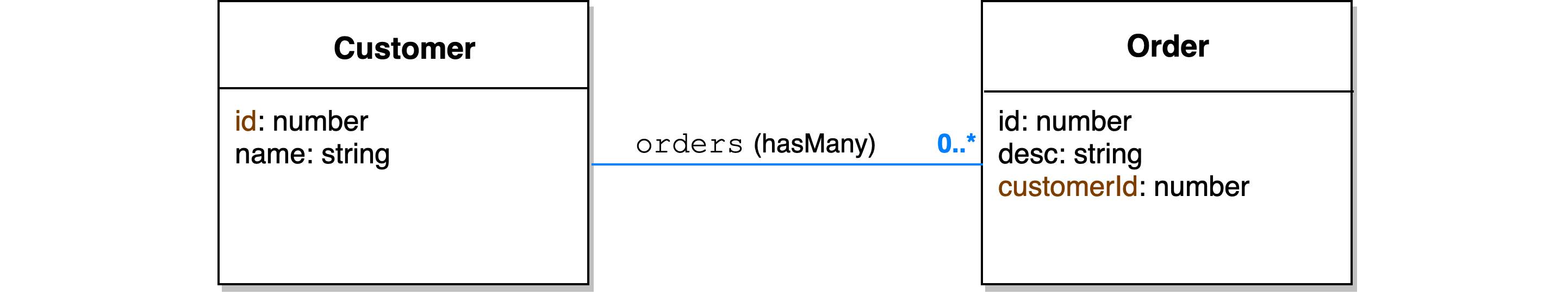
If we'd like to get a customer's instance with all their orders instances, we can query on Customer with filter {include: [{relation: 'orders']}. The inclusion resolvers are similar to GraphQL resolvers -- it will find the target instances of Customer first and pass its result to the inclusion resolver of orders. The query result will contain the return value of orders nested under corresponding Customer instead of connecting to database twice. Read on for detailed examples and explanations!
LoopBack 4 creates a different inclusion resolver for each relation type. Each relation has its own inclusion resolver inclusionResolver. And each repository has a built-in property inclusionResolvers as a registry for its inclusionResolvers.
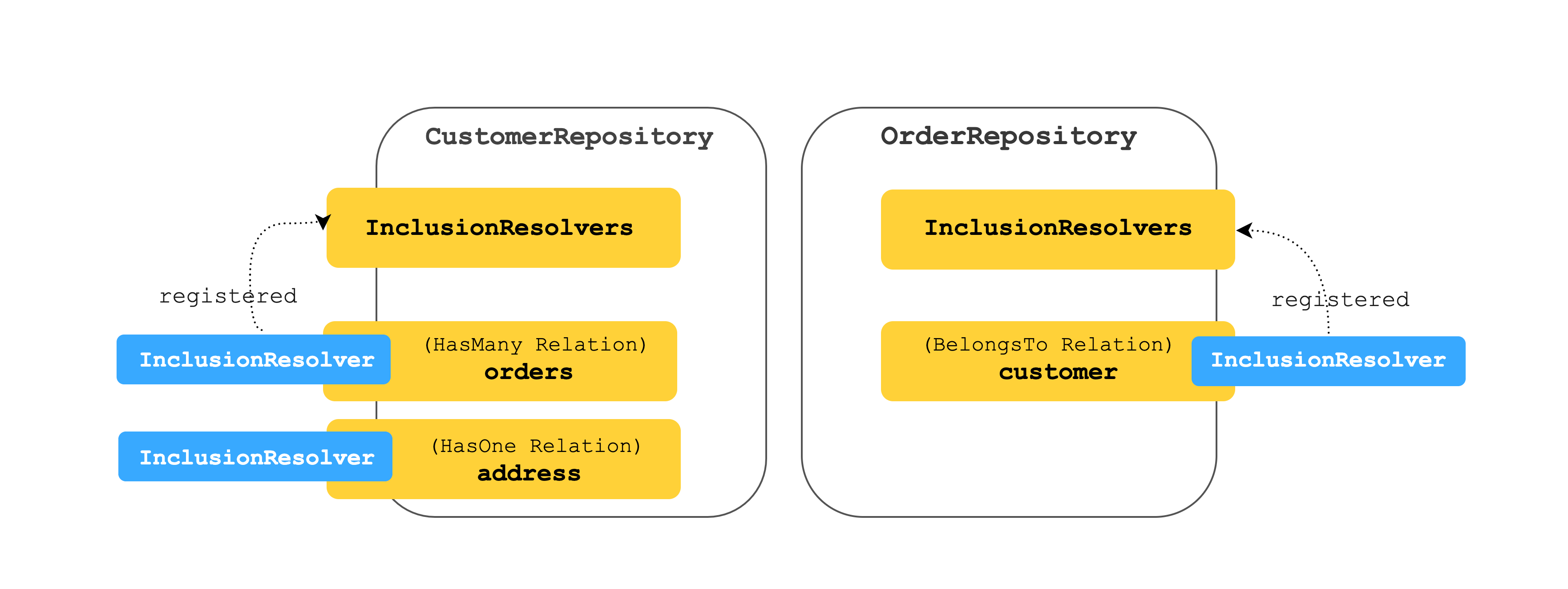
To enable querying related models for a certain relation, the corresponding inclusionResolver of that relation has to be registered to the inclusionResolvers. I promise the set up is not as complicated as what you just read through.
Let me show you the steps to enable this feature in few steps!
0. Before you get started
Upgrade your global installation of LoopBack 4 command line interface (CLI) to get the new feature.
$ npm install -g "@loopback/cli"
1. Set up models and datasource
You can set up models and datasource by the CLI lb4 model and lb4 datasouce.
I use MySQL as my database in this case. And here are my models Customer and Order:
customer.model.ts:
// imports
@model()
export class Customer extends Entity {
@property({
id: true,
generated: true
})
id: number;
@property({
type: "string"
})
name: string;
// constructor
}
order.model.ts:
@model()
export class Order extends Entity {
@property({
id: true,
generated: true
})
id: number;
@property({
type: "string",
required: true
})
description: string;
}
//constructor
2. Set up relations and register inclusion resolver for each relation
We are setting up two relations in this example:
hasMany: aCustomerhas manyOrders. Named this relation asorders.belongsTo: anOrderhas aCustomer. Named this relation ascustomer. The foreign key iscustomerId.
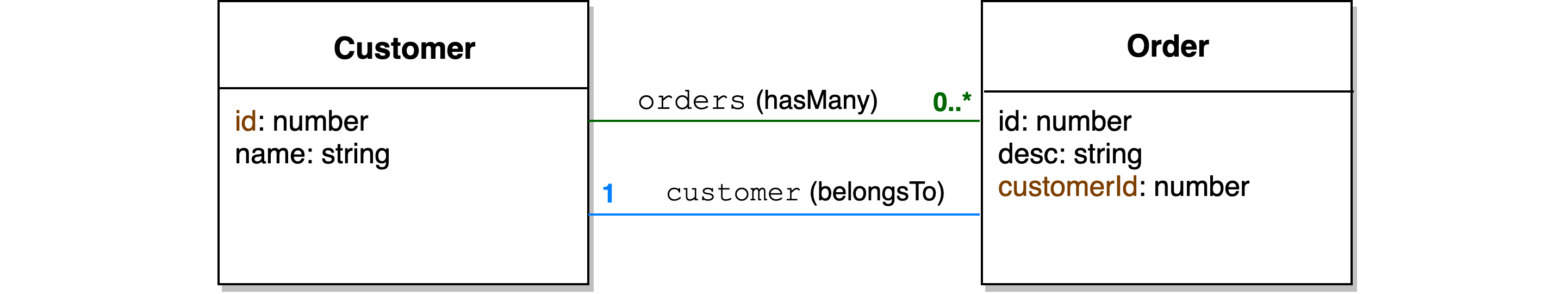
You can either modify your model and repository files or use CLI lb4 relation to set up relations and enable the inclusionResolver in each relation. Here's how I set the belongsTo relation through the CLI:
$ lb4 relation
? Please select the relation type: belongsTo
? Please select source model: Order
? Please select target model: Customer
? Source property name for the relation getter: customerId
? Allow Order queries to include data from related Customer instances? Yes
create src/controllers/order-customer.controller.ts
Relation BelongsTo was created in src/
This prompt registers the inclusionResolver for this belongsTo relation for you.
? Allow Order queries to include data from related Customer instances? (Y/n)
It defaults to Yes. Make sure to choose 'yes' if you'd like to use inclusion and your model is traversable.
Here is the code snippet for models after setting up two relations and enabling both inclusion resolvers:
customer.model.ts:
// imports
@model()
export class Customer extends Entity {
// id, name properties
@hasMany(() => Order)
orders?: Order[];
// constructor
}
order.model.ts:
// imports
@model()
export class Order extends Entity {
// id, desc properties
@belongsTo(() => Customer)
customerId: Customer;
}
//constructor
And you'll see the inclusion resolvers are enabled in the repository classes:
customer.repository.ts:
//imports
export class CustomerRepository extends DefaultCrudRepository {
public readonly orders: HasManyRepositoryFactory<
Order,
typeof Customer.prototype.id
>;
constructor(
dataSource: DbDataSource,
orderRepositoryGetter: Getter<OrderRepository>
) {
super(Customer, dataSource);
this.orders = this.createHasManyRepositoryFactoryFor(
"orders",
orderRepositoryGetter
);
// this line registers inclusion resolver, allows us to query related models
this.registerInclusionResolver("orders", this.orders.inclusionResolver);
}
}
order.repository.ts:
export class OrderRepository extends DefaultCrudRepository {
public readonly customer: BelongsToAccessor<
Customer,
typeof Order.prototype.id
>;
constructor(
dataSource: juggler.DataSource,
customerRepositoryGetter: Getter<CustomerRepository>
) {
super(Order, dataSource);
this.customer = this.createBelongsToAccessorFor(
"customer",
customerRepositoryGetter
);
// this line registers inclusion resolver, allows us to query related models
this.registerInclusionResolver("customer", this.customer.inclusionResolver);
}
}
Notice: I use default values in this example. We also recommend to follow the naming convention. If you'd like to custom property names or relation names, check our site Relations for more details.
3. Try it out!
At this point, you're able to query related models by specifying the relation name in the inclusion field. Let's create instances for Customer and Order.
Customer: [
{id: 1, name: `Thor`},
{id: 2, name: `Captain`},
],
Order: [
{id: 1, desc: `Rocket Raccoon`, customerId: 1},
{id: 2, desc: `Shield`, customerId: 2},
{id: 3, desc: `Mjolnir`, customerId: 1},
]
You can either query data via controllers or do it in the repository level.
export class CustomerController {
// constructor
@get('/customers', {
...
}
export class OrderController {
// constructor
@get('/orders', {
...
}
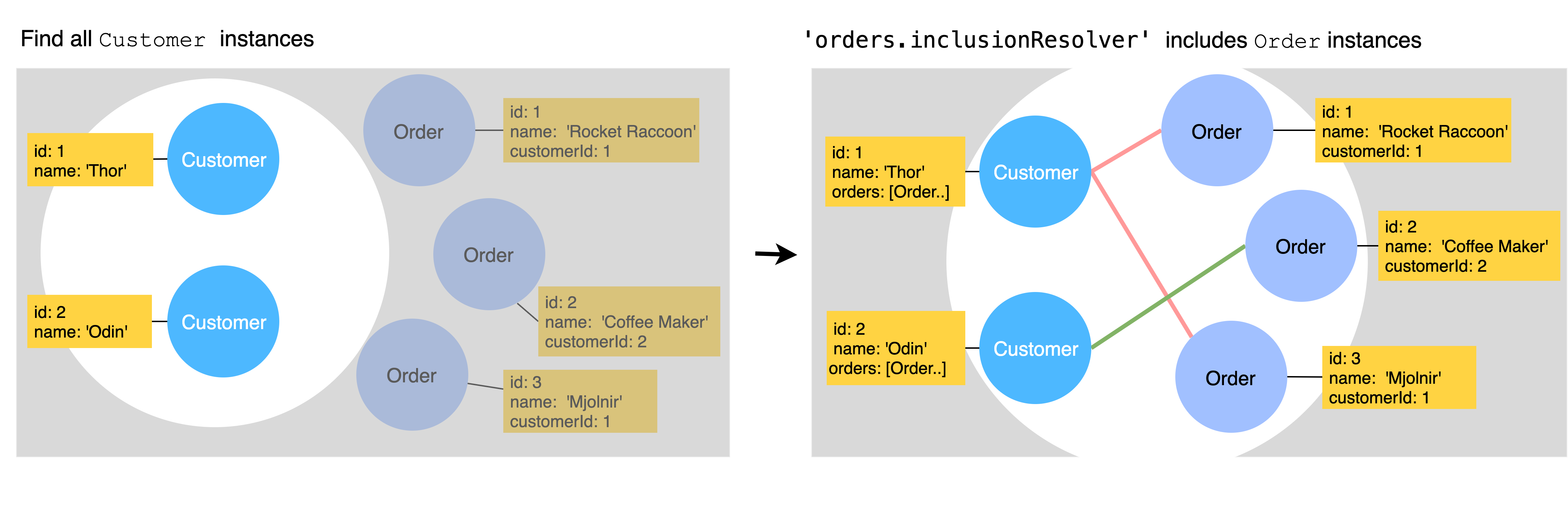
For hasMany relation orders, these queries return all customers with their Orders:
-
Use controllers (or use the API Explorer
http://localhost:3000/explorer/):GET http://localhost:3000/customers?filter[include][][relation]=orders -
This is the same as you process data in the repository level:
await customerRepository.find({ include: [{ relation: "orders" }] });
Result:
[
{
id: 1,
name: 'Thor',
orders: [
{id: 1, desc: 'Mjolnir', customerId: 1},
{id: 3, desc: 'Rocket Raccoon', customerId: 1},
],
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Captain',
orders: [{id: 2, desc: 'Shield', customerId: 2}],
},
];
Here is a diagram to make this more intuitive:
For belongsTo relation customer, these queries return the Order that has id = 1 and includes the Customer it belongs to.
-
Use controllers (or use the API Explorer
http://localhost:3000/explorer/):GET http://localhost:3000/orders/1?filter[include][][relation]=customer -
This is the same as you process data in the repository level:
await orderRepository.findById(1, {include: [{relation: 'customer'}]};)
Result:
[
{
id: 1,
desc: 'Rocket Raccoon',
customerId: 1,
customer: {id: 1, name: 'Thor'},
},
]
Besides the example I've shown above, our TodoList Tutorial example also uses inclusion. Check on the site for more detailed steps.
Hope this new feature is helpful for you!
Limitations
Though we've finished the implementation of this new feature and test it against SQL and NoSQL databases, there are some limitations:
- Including related models with a custom scope is not supported. For example, for
ordersof aCustomer, it cannot filter a certainOrders that you want to include inorders. Related GH issue: Include related models with a custom scope - We don't support recursive inclusion of related models. Related GH issue: Recursive inclusion of related models
- It doesn't split numbers of queries. Related GH issue: Support
inqsplitting. - It might not work well with
ObjectIdof MongoDB. Related GH issue: Spike: robust handling of ObjectID type for MongoDB
We have some discussions on these issues. Please check out the Post MVP Enhancement story if you're interested. We'd love to hear your input and feel free to contribute.
Thanks for choosing LoopBack!
Call to Action
LoopBack's success depends on you! We appreciate your continuous support and engagement to make LoopBack even better and meaningful for your API creation experience. Here's how you can join us and help the project:
- Report issues.
- Contribute code and documentation.
- Open a pull request on one of our "good first issues".
- Join our user group.