Overview
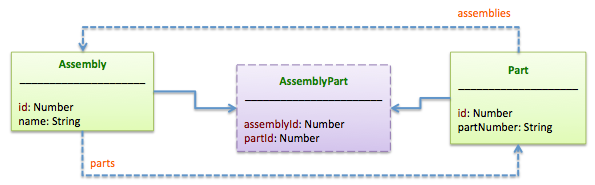
A hasAndBelongsToMany relation creates a direct many-to-many connection with another model, with no intervening model. For example, in an application with assemblies and parts, where each assembly has many parts and each part appears in many assemblies, you could declare the models this way:
Defining a hasAndBelongsToMany relation
Use apic loopback:relation to create a relation between two models. The tool will prompt you to enter the name of the model, the name of related model, and other required information.
The tool will then modify the model definition JSON file (for example, common/models/customer.json) accordingly.
Use slc loopback:relation to create a relation between two models. The tool will prompt you to enter the name of the model, the name of related model, and other required information.
The tool will then modify the model definition JSON file (for example, common/models/customer.json) accordingly.
For more information, see Relation generator.
 </figure>
</figure>
For example, here is an excerpt from a model JSON file for an assembly model, expressing a hasAndBelongsToMany relation between assembly and part models:
/common/models/assembly.json
{
"name": "Assembly",
"plural": "Assemblies",
"relations": {
"parts": {
"type": "hasAndBelongsToMany",
"model": "Part",
"throughTable": "AssemblyPart"
},
...
If needed, you can use the “throughTable” field to define a custom table name for the relation.
You can also define a hasAndBelongsToMany relation in code, though this is not recommended in general. For example:
/common/models/assembly.js
Part.hasAndBelongsToMany(Assembly);
Assembly.hasAndBelongsToMany(Part);
Adding a relation via REST API
When adding relation through the REST API, a join model must exist before adding relations. For Example in the above example with “Assembly” and “Part” models, to add an instance of “Part” to “Assembly” through the REST API interface an “AssemblyPart” model must exist for it to work.
Most of the time you should add “hasAndBelongToMany” relations to models on server side using the method:
Example method
assembly.parts.add(part, function(err) {
//...
});
Thus, if you need to add the relation using REST, first check if the “AssemblyPart” model exists first. Then add the relation using this code:
Rest Example Method
Assembly.Parts.link({id:assemblyId, fk: partId}, partInstance, function(value, header) {
//success
});
Methods added to the model
Once you define a “hasAndBelongsToMany” relation, LoopBack adds methods with the relation name to the declaring model class’s prototype automatically.
For example: assembly.parts.create(...).
| Example method | Description |
|---|---|
assembly.parts(filter,
function(err, parts) {
|
Find parts for the assembly. |
var part = assembly.parts.build(data); |
Build a new part. |
assembly.parts.create(data,
function(err, part) {
|
Create a new part for the assembly. |
assembly.parts.add(part,
function(err) {
|
Add a part to the assembly. |
assembly.parts.remove(part,
function(err) {
|
Remove a part from the assembly. |
assembly.parts.findById(partId,
function(err, part) {
|
Find a part by ID. |
assembly.parts.destroy(partId,
function(err) {
|
Delete a part by ID. |