Overview
A hasManyThrough relation sets up a many-to-many connection with another model.
This relation indicates that the declaring model can be matched with zero or more instances of another model by proceeding through a third model.
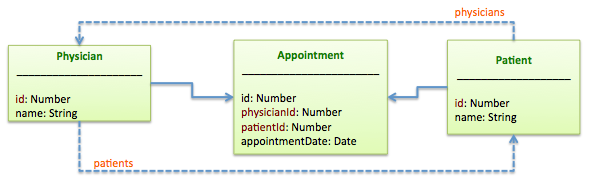
For example, in an application for a medical practice where patients make appointments to see physicians, the relevant relation declarations might be:
 </figure>
</figure>
The “through” model, Appointment, has two foreign key properties, physicianId and patientId, that reference the primary keys in the declaring model, Physician, and the target model, Patient.
Defining a hasManyThrough relation
Use apic loopback:relation to create a relation between two models.
The tool will prompt you to enter the name of the model, the name of related model, and other required information.
The tool will then modify the model definition JSON file (for example, common/models/customer.json) accordingly.
Use slc loopback:relation to create a relation between two models.
The tool will prompt you to enter the name of the model, the name of related model, and other required information.
The tool will then modify the model definition JSON file (for example, common/models/customer.json) accordingly.
For more information, see Relation generator.
To create a hasManyThrough relation, respond with Yes to the prompt for a “through” model, then specify the model:
[?] Require a through model? Yes
[?] Choose a through model: Appointment
For example:
common/models/physician.json
{
"name": "Physician",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"patients": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Patient",
"foreignKey": "physicianId",
"through": "Appointment"
},
...
common/models/patient.json
{
"name": "Patient",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"physicans": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Physician",
"foreignKey": "patientId",
"through": "Appointment"
},
...
common/models/appointment.json
{
"name": "Appointment",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"appointmentDate": {
"type": "date"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"physician": {
"type": "belongsTo",
"model": "Physician",
"foreignKey": "physicianId"
},
"patient": {
"type": "belongsTo",
"model": "Patient",
"foreignKey": "patientId"
},
...
You can also define a hasManyThrough relation in code, though this is not generally recommended:
common/models/physician.js
//...
Appointment.belongsTo(Patient);
Appointment.belongsTo(Physician);
Physician.hasMany(Patient, {through: Appointment});
Patient.hasMany(Physician, {through: Appointment});
// Now the Physician model has a virtual property called patients:
Physician.patients(filter, callback); // Find patients for the physician
Physician.patients.build(data); // Build a new patient
Physician.patients.create(data, callback); // Create a new patient for the physician
Physician.patients.destroyAll(callback); // Remove all patients for the physician
Physician.patients.add(patient, callback); // Add an patient to the physician
Physician.patients.remove(patient, callback); // Remove an patient from the physician
Physician.patients.findById(patientId, callback); // Find an patient by id
Defining the foreign key property
A hasManyThrough relation has a keyThrough property that indicates the foreign key property (field) name. If not specified, it defaults to the toModelName with Id appended; for example:
Physician.hasMany(Patient, {through: Appointment})-keyThroughdefaults topatientId.Patient.hasMany(Physician, {through: Appointment})-keyThroughdefaults tophysicianId.
The keyThrough properties above will be used to match these foreignKeys below:
Appointment.belongsTo(Physician, {as: 'foo', foreignKey: 'physicianId'});
Appointment.belongsTo(Patient, {as: 'bar', foreignKey: 'patientId'});
You can specify the keyThrough property explicitly:
Physician.hasMany(Patient, {through: Appointment, foreignKey: 'fooId', keyThrough: 'barId'});
Patient.hasMany(Physician, {through: Appointment, foreignKey: 'barId', keyThrough: 'fooId'});
// keyThroughs above will be used to match foreignKeys below
Appointment.belongsTo(Physician, {as: 'foo'}); // foreignKey defaults to 'fooId'
Appointment.belongsTo(Patient, {as: 'bar'}); // foreignKey defaults to 'barId'
keyThrough in JSON
Here is an example of defining a hasManyThrough relation with foreign keys. Consider the following tables:
- STUDENTS(ID,STUNAME): student information
- COURSES(ID,COURNAME): course information
- COURSTU(COURID,STUID): table with foreign keys that handle the many-to-many mapping
You can define the relations in JSON files in common/models as follows:
common/models/courses.json
...
"relations": {
"students": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Students",
"foreignKey": "courid",
"through": "Courstu",
"keyThrough": "stuid"
}
...
common/models/students.json
"relations": {
"courses": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Courses",
"foreignKey": "stuid",
"through": "Courstu",
"keyThrough": "courid"
}
Self through
In some cases, you may want to define a relationship from a model to itself. For example, consider a social media application where users can follow other users.
In this case, a user may follow many other users and may be followed by many other users. The code below shows how this might be defined, along with corresponding keyThrough properties:
common/models/user.js
User.hasMany(User, {as: 'followers', foreignKey: 'followeeId', keyThrough: 'followerId', through: Follow});
User.hasMany(User, {as: 'following', foreignKey: 'followerId', keyThrough: 'followeeId', through: Follow});
Follow.belongsTo(User, {as: 'follower'});
Follow.belongsTo(User, {as: 'followee'});
Methods added to the model
Once you define a “hasManyThrough” relation, LoopBack adds methods with the relation name to the declaring model class’s prototype automatically, for example: physician.patients.create(...).
| Example method | Description |
|---|---|
physician.patients(filter,
function(err, patients) {
|
Find patients for the physician. |
var patient = physician.patients.build(data); |
Create a new patient. |
physician.patients.create(data,
function(err, patient) {
|
Create a new patient for the physician. |
physician.patients.destroyAll(function(err) {
|
Remove all patients for the physician |
physician.patients.add(patient,
function(err, patient) {
|
Add a patient to the physician. |
physician.patients.remove(patient,
function(err) {
|
Remove a patient from the physician. |
physician.patients.findById(patientId,
function(err, patient) {
|
Find an patient by ID. |
These relation methods provide an API for working with the related object (patient in the example above). However, they do not allow you to access both the related object (Patient) and the “through” record (Appointment) in a single call.
For example, if you want to add a new patient and create an appointment at a certain date, you have to make two calls (REST requests):
-
Create the patient via
Patient.createPOST /patients{ "name": "Jane Smith" } -
Create the appointment via
Appointment.create, setting thepatientIdproperty to theidreturned byPatient.create.POST /appointments{ "patientId": 1, "physicianId": 1, "appointmentDate": "2014-06-01" }
The following query can be used to list all patients of a given physician, including their appointment date:
GET /appointments?filter={"include":["patient"],"where":{"physicianId":2}}
Sample response:
[
{
"appointmentDate": "2014-06-01",
"id": 1,
"patientId": 1,
"physicianId": 1,
"patient": {
"name": "Jane Smith",
"id": 1
}
}
]