See also:
Important: To use this component, you should be familiar with Passport
Overview
The loopback-component-passport module integrates Passport and supports:
-
Third-party login, so LoopBack apps can allow users to login using existing accounts on Facebook, Google, Twitter, Github, and others.
-
Integration with enterprise security services so that users can login with them instead of username and password-based authentication.
-
Linking an account authorized through one of the above services with a LoopBack application user record. This enables you to manage and control your own user account records while still integrating with third-party services.
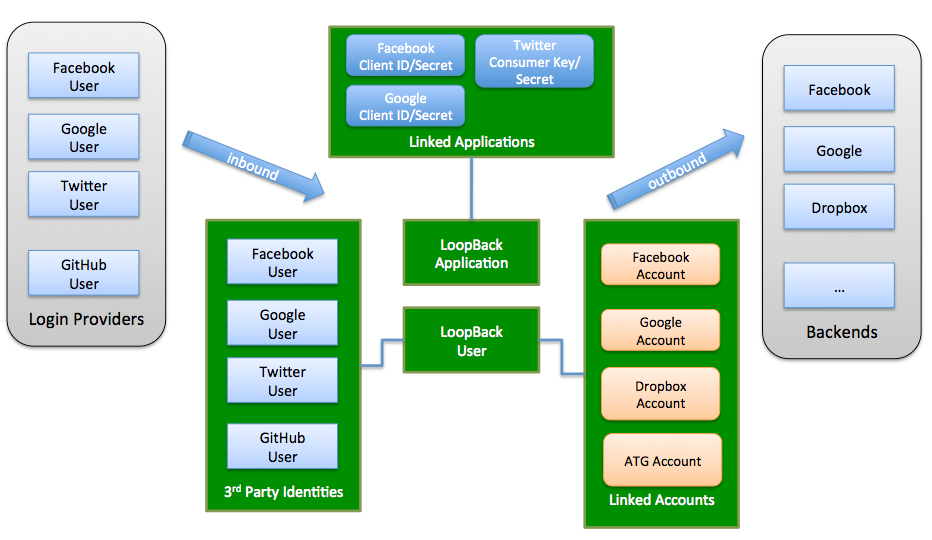 </figure>
</figure>
This module includes:
-
UserIdentity model - keeps track of third-party login profiles.
-
UserCredential model - stores credentials from a third-party provider to represent users’ permissions and authorizations.
-
ApplicationCredential model - stores credentials associated with a client application.
-
PassportConfigurator - the bridge between LoopBack and Passport.
The example application demonstrates how to implement third-party login with a LoopBack application.
Installation
Install the third-party login (Passport) component as usual for a Node package:
$ npm install loopback-component-passport
Models
UserIdentity model
The UserIdentity model keeps track of third-party login profiles. Each user identity is uniquely identified by provider and externalId. The UserIdentity model has a belongsTo relation to the User model.
The following table describes the properties of the UserIdentity model.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| provider | String | Auth provider name; for example facebook, google, twitter, or linkedin. |
| authScheme | String | auth scheme, such as oAuth, oAuth 2.0, OpenID, OpenID Connect |
| externalId | String | Provider specific user ID. |
| profile | Object | User profile, see http://passportjs.org/guide/profile |
| credentials | Object | User credentials
|
| userId | Any | LoopBack user ID |
| created | Date | Created date |
| modified | Date | Last modified date |
UserCredential model
UserCredential has the same set of properties as UserIdentity. It’s used to store the credentials from a third party authentication/authorization provider to represent the permissions and authorizations of a user in the third-party system.
ApplicationCredential model
Interacting with third-party systems often requires client application level credentials. For example, you need oAuth 2.0 client ID and client secret to call Facebook APIs. Such credentials can be supplied from a configuration file to your server globally. But if your server accepts API requests from multiple client applications, each client application needs its own credentials. The ApplicationCredential model stores credentials associated with the client application, to support multi-tenancy.
The ApplicationCredential model has a belongsTo relation to the Application model.
The following table describes the properties of ApplicationCredential model
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| provider | String | Auth provider name, such as facebook, google, twitter, linkedin |
| authScheme | String | Auth scheme, such as oAuth, oAuth 2.0, OpenID, OpenID Connect |
| credentials | Object | Provider-specific credentials:
|
| created | Date | Created date |
| modified | Date | Last modified date |
PassportConfigurator
PassportConfigurator is the bridge between LoopBack and Passport. It:
- Sets up models with LoopBack
- Initializes passport
- Creates Passport strategies from provider configurations
- Sets up routes for authorization and callback
Login and account linking
Third party login
The following steps use Facebook oAuth 2.0 login as an example. The basic procedure is:
- A visitor requests to log in using Facebook by clicking on a link or button backed by LoopBack to initiate oAuth 2.0 authorization.
- LoopBack redirects the browser to Facebook’s authorization endpoint so the user can log into Facebook and grant permissions to LoopBack
- Facebook redirects the browser to a callback URL hosted by LoopBack with the oAuth 2.0 authorization code
- LoopBack makes a request to the Facebook token endpoint to get an access token using the authorization code
- LoopBack uses the access token to retrieve the user’s Facebook profile
- LoopBack searches the UserIdentity model by (provider, externalId) to see there is an existing LoopBack user for the given Facebook id
- If yes, set the LoopBack user to the current context
- If not, create a LoopBack user from the profile and create a corresponding record in UserIdentity to track the 3rd party login. Set the newly created user to the current context.
Linking third-party accounts
Follow these steps to link LoopBack accounts using Facebook oAuth 2.0:
- The user logs into LoopBack first directly or through third-party login.
- The user clicks on a link or button to start the oAuth 2.0 authorization so that the user can grant permissions to LoopBack.
- Perform steps 2-5 in third-party login, above.
- LoopBack searches the UserCredential model by (provider, externalId) to see if there is an existing LoopBack user for the given Facebook ID.
- Link the Facebook account to the current user by creating a record in the UserCredential model to store the Facebook credentials, such as access token.
- Now the LoopBack user wants to get a list of pictures from the linked Facebook account(s). LoopBack can look up the Facebook credentials associated with the current user and use them to call Facebook APIs to retrieve the pictures.
Configuring third-party providers
Important:
You must register with Facebook and Google to get your own client ID and client secret.
The following example illustrates using two providers:
- facebook-login for login with Facebook
- google-link for linking Google accounts with the current LoopBack user.
- ms-ad for linking LDAP records using Microsoft Active Directory. NOTE: This is an early release of support this provider.
Configuration in providers.json
Use providers.json (in project root directory) to set up the external authentication providers.
For more information, see Configuring providers.json. Here’s an example:
providers.json
{
"facebook-login": {
"provider": "facebook",
"module": "passport-facebook",
"clientID": "{facebook-client-id-1}",
"clientSecret": "{facebook-client-secret-1}",
"callbackURL": "http://localhost:3000/auth/facebook/callback",
"authPath": "/auth/facebook",
"callbackPath": "/auth/facebook/callback",
"successRedirect": "/auth/account",
"scope": ["email"]
},
...
"google-link": {
"provider": "google",
"module": "passport-google-oauth",
"strategy": "OAuth2Strategy",
"clientID": "{google-client-id-2}",
"clientSecret": "{google-client-secret-2}",
"callbackURL": "http://localhost:3000/link/google/callback",
"authPath": "/link/google",
"callbackPath": "/link/google/callback",
"successRedirect": "/link/account",
"scope": ["email", "profile"],
"link": true
},
...
"ms-ad": {
"provider": "ms-ad",
"authScheme":"ldap",
"module": "passport-ldapauth",
"authPath": "/auth/msad",
"successRedirect": "/auth/account",
"failureRedirect": "/msad",
"failureFlash": true,
"session": true,
"LdapAttributeForLogin": "mail",
"LdapAttributeForUsername": "mail",
"LdapAttributeForMail": "mail",
"server":{
"url": "ldap://ldap.example.org:389/dc=example,dc=org",
"bindDn": "bindUsername",
"bindCredentials": "bindPassword",
"searchBase": "ou=people,dc=example,dc=org",
"searchAttributes": ["cn", "mail", "uid", "givenname"],
"searchFilter": "(&(objectcategory=person)(objectclass=user)(|(samaccountname=)(mail=)))"
}
},
...
}
Set up in application code
Add code such as the following to server/server.js to load provider configurations, as illustrated in
loopback-example-passport.
The following example code:
- Creates an instance of
PassportConfigurator. - Loads the provider configurations shown above.
- Initializes Passport.
- Sets up related models.
- Configures Passport strategies for third-party auth providers.
var loopback = require('loopback');
var path = require('path');
var app = module.exports = loopback();
// Create an instance of PassportConfigurator with the app instance
var PassportConfigurator = require('loopback-component-passport').PassportConfigurator;
var passportConfigurator = new PassportConfigurator(app);
app.boot(__dirname);
...
// Enable http session
app.use(loopback.session({ secret: 'keyboard cat' }));
// Load the provider configurations
var config = {};
try {
config = require('./providers.json');
} catch(err) {
console.error('Please configure your passport strategy in `providers.json`.');
console.error('Copy `providers.json.template` to `providers.json` and replace the clientID/clientSecret values with your own.');
process.exit(1);
}
// Initialize passport
passportConfigurator.init();
// Set up related models
passportConfigurator.setupModels({
userModel: app.models.user,
userIdentityModel: app.models.userIdentity,
userCredentialModel: app.models.userCredential
});
// Configure passport strategies for third party auth providers
for(var s in config) {
var c = config[s];
c.session = c.session !== false;
passportConfigurator.configureProvider(s, c);
}
Customize Loopback User created
Some users might need to configure the Loopback users created by the component if the UniqueID provided comes in an email format (see issue for details),
this can be configured by passing in options in passportConfigurator.configureProvider(), User will need to provide their own function
to build their Loopback User object similar to following example, then provide it in options of passportConfigurator.configureProvider()
function customProfileToUser(provider, profile, options) {
var userInfo = {
username: profile.username,
password: 'secret',
email: profile.email,
};
return userInfo;
}
//following loopback-example-passport's server.js
var config = require('../providers.json');
for (var s in config) {
var c = config[s];
c.session = c.session !== false;
// overriding default user object
c.profileToUser = customProfileToUser;
passportConfigurator.configureProvider(s, c);
}