Overview
Wikipedia: Authorization is the function of specifying access rights/privileges to resources
LoopBack’s highly extensible authorization package @loopback/authorization provides various features and provisions to check access rights of a client on a API endpoint.
API clients login to get a credential (can be a token, api-key, claim or cert). When the client calls an API endpoint, they pass the credential in the request to identify themselves (Authentication) as well as claim their access rights (Authorization).
LoopBack’s authorization component checks if the permissions associated with the credential provided by the client satisfies the accessibility criteria defined by the users.
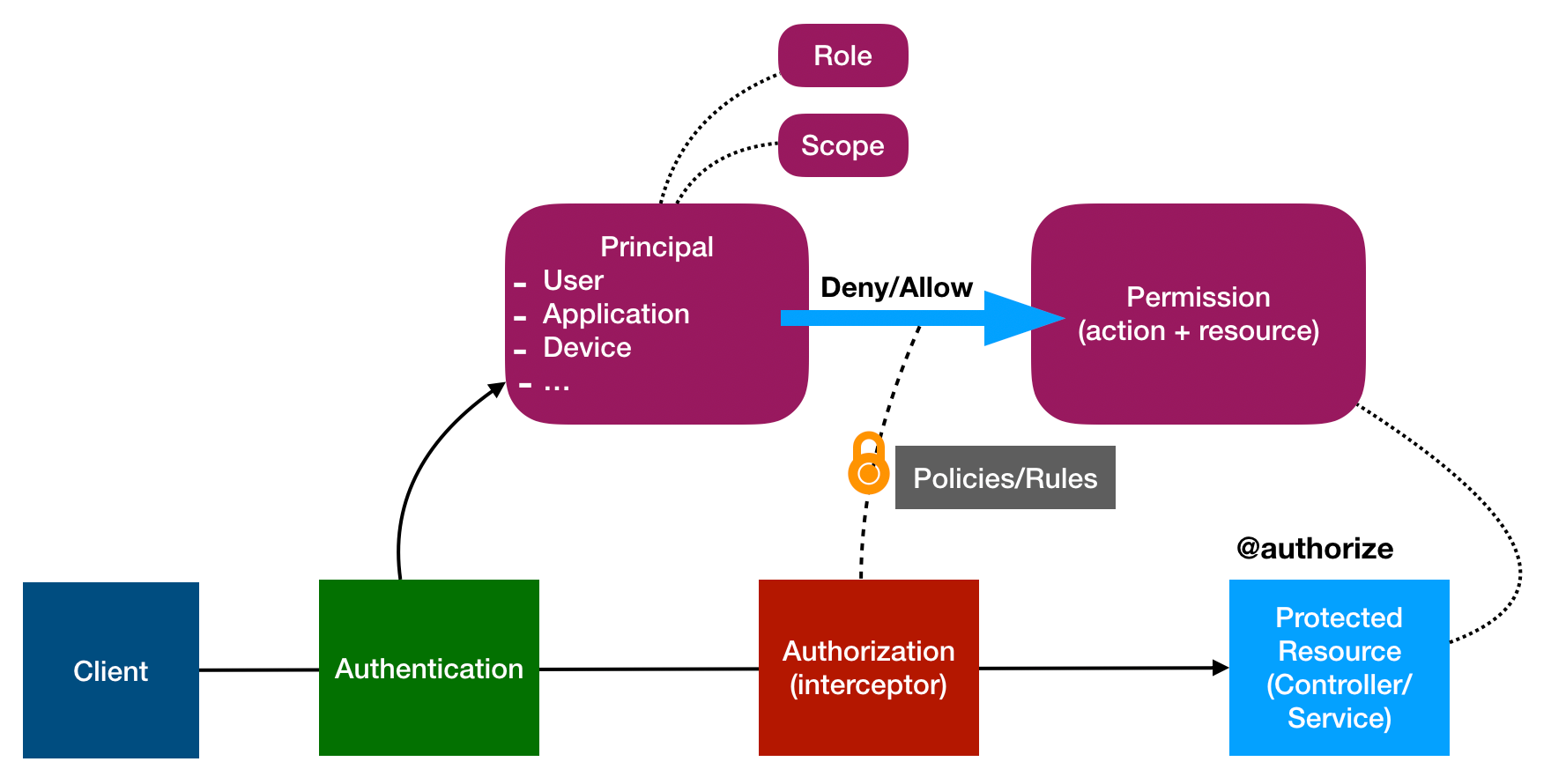
Design
A Principal could be a User, Application or Device. The Principal is
identified from the credential provided by a client, by the configured
Authentication strategy of the endpoint
(see, LoopBack Authentication). Access
rights of the client is either associated with or included in the credential.
The Principal is then used by LoopBack’s authorization mechanism to enforce
necessary privileges/access rights by using the permissions annotated by the
@authorize decorator on the controller methods.
The expectations from various stake holders (LoopBack, Architects, Developers) for implementation of the authorization features are given below in the Chain of Responsibility section.
Chain of Responsibility
LoopBack as a framework provides certain provisions and expects the developers to extend with their specific implementations. Architects or Security analysts generally provide security policies to clarify how the developers should approach authorization.
The framework provides,
- the
@authorizedecorator to provide authorization metadata and voters - various
typesandinterfacesto declare user providedartifacts - a mechanism to enforce authorization policies
- abstractions of
authorizersas user provided functions and voters - create a decision matrix to combine results of all user provided
authorizers - an interceptor which enforces policies by creating the decision matrix
- abstractions of
- a LoopBack authorization component which packs all the above
Architects should,
- separate global authorization concerns as
authorizers - identify specific responsibilities of an endpoint as
voters - provide security policies for conflicting decisions from
authorizersandvoters - provide authentication policies with necessary scopes and roles for every endpoint
Developers need to,
- mount the authorization component, see Registering the Authorization Component
- decorate endpoints with authorization metadata, see Configuring API Endpoints
- define
authorizerandvoterfunctions, see Programming Access Policies - design security policies as decision matrix, see Authorization by decision matrix
- plug in external enforcer libraries, see Enforcer Libraries
Tutorials
-
Building RBAC system with @loopback/authorization: A tutorial for beginners to get started with the concepts and responsibilities.
-
Using component
@loopback/authorization: The instructions of how to apply component@loopback/authorization.