Overview
This document describes the details of the LoopBack 4 Authentication component
from the @loopback/authentication package.
It begins with the architecture of @loopback/authentication from high level.
Then comes with the sub-sections for each artifact provided by the component.
Each section shows:
- How to use it in the application. (Code that users need to add when using the module.)
- The mechanism of that artifact. (Code that explains the mechanism.)
Here is a high level overview of the authentication component.
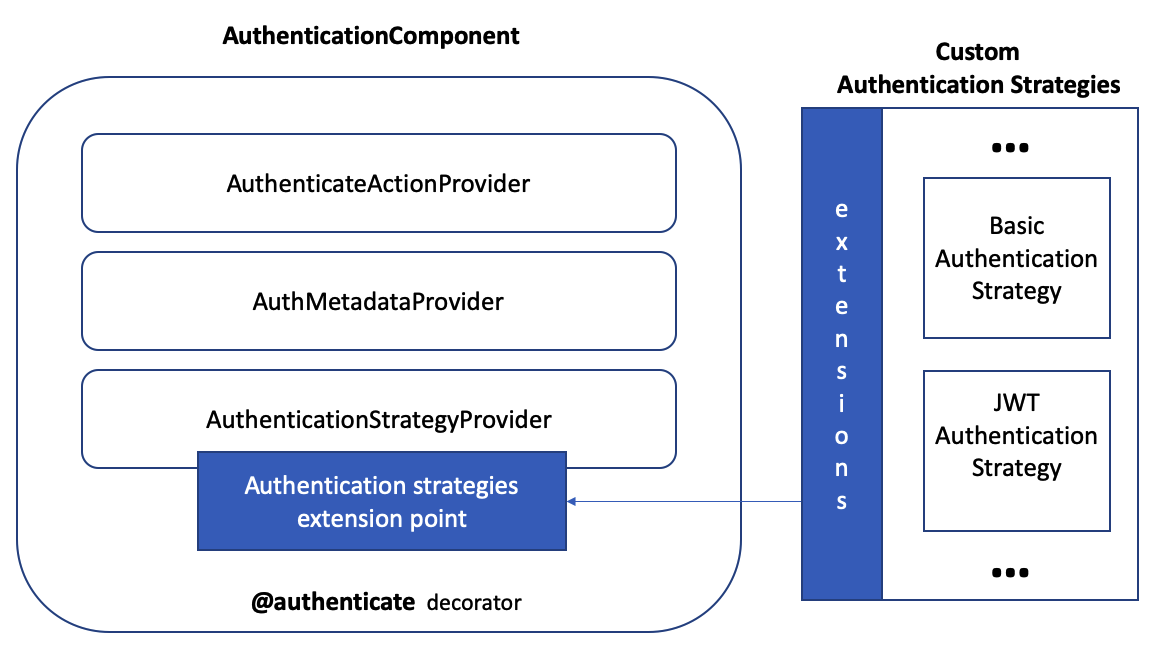
As illustrated in the diagram, this component includes:
- A decorator to express an authentication requirement on controller methods
- A provider to access method-level authentication metadata
- An action in the REST sequence to enforce authentication
- An extension point to discover all authentication strategies and handle the delegation
Then let’s take a look of the detailed overview of the authentication component.
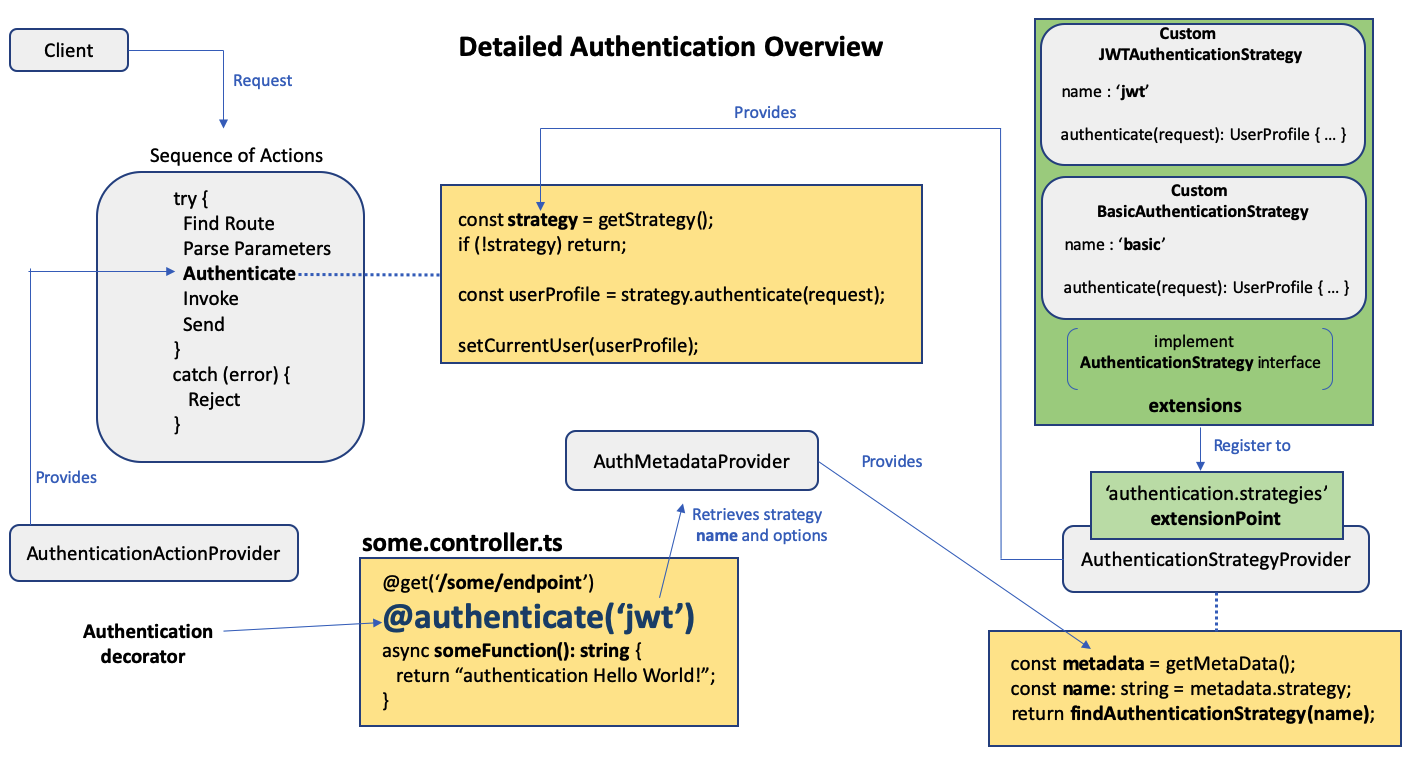
Basically, to secure your API endpoints, you need to:
- decorate the endpoints of a controller with the
@authenticate(strategyName, options?)decorator (app developer) - insert the authentication action in a custom sequence (app developer)
- create a custom authentication strategy with a unique name (extension developer)
- register the custom authentication strategy (app developer)
The Authentication Component takes care of the rest.
Installation
npm install --save @loopback/authentication
Mounting Authentication Component
To utilize authentication in an application application.ts, you must load
the authentication component named AuthenticationComponent.
import {AuthenticationComponent} from '@loopback/authentication';
//...
export class MyApplication extends BootMixin(
ServiceMixin(RepositoryMixin(RestApplication)),
) {
constructor(options?: ApplicationConfig) {
super(options);
//...
// ------ ADD SNIPPET AT THE BOTTOM ---------
// Mount authentication system
this.component(AuthenticationComponent);
// ------------- END OF SNIPPET -------------
//...
}
}
The AuthenticationComponent is defined as follows:
// ------ CODE THAT EXPLAINS THE MECHANISM ---------
export class AuthenticationComponent implements Component {
providers?: ProviderMap;
constructor() {
this.providers = {
[AuthenticationBindings.AUTH_ACTION.key]: AuthenticateActionProvider,
[AuthenticationBindings.STRATEGY.key]: AuthenticationStrategyProvider,
[AuthenticationBindings.METADATA.key]: AuthMetadataProvider,
};
}
}
As you can see, there are a few providers which make up the bulk of the authentication component.
Essentially
- The binding key
AuthenticationBindings.METADATA.keyis bound toAuthMetadataProviderwhich returns authentication decorator metadata of typeAuthenticationMetadata - The binding key
AuthenticationBindings.AUTH_ACTION.keyis bound toAuthenticateActionProviderwhich returns an authenticating function of typeAuthenticateFn - The binding key
AuthenticationBindings.STRATEGY.keyis bound toAuthenticationStrategyProviderwhich resolves and returns an authentication strategy of typeAuthenticationStrategy
The purpose of these providers and the values they return will be explained in the sections below.
Navigation
Next topic: Authentication Decorator