This page describes the middleware-based sequence for REST server.
What is a Sequence?
A Sequence is a series of steps to control how a specific type of Server
responds to incoming requests. Each types of servers, such as RestServer,
GraphQLServer, GRPCServer, and WebSocketServer, will have its own flavor of
sequence. The sequence represents the pipeline for inbound connections.
The contract of a Sequence is simple: it must produce a response for a
request. The signature will vary by server types.
Each server type has a default sequence. It’s also possible to create your own
Sequence to have full control over how your Server instances handle requests
and responses.
The default sequence
Warning: Since version 6.0.0 of @loopback/rest, we have switched to a middleware-based
sequence as the default for flexibility, composability, and consistency. See Common Task to learn how to migrate your legacy Sequence
When a LoopBack application is scaffolded using lb4 app command, a
MySequence class is generated in src/sequence.ts.
import {MiddlewareSequence} from '@loopback/rest';
export class MySequence extends MiddlewareSequence {}
MySequence is then used by the RestApplication in src/application.ts:
import {BootMixin} from '@loopback/boot';
import {ApplicationConfig} from '@loopback/core';
import {RepositoryMixin} from '@loopback/repository';
import {RestApplication} from '@loopback/rest';
import {ServiceMixin} from '@loopback/service-proxy';
import {MySequence} from './sequence';
export {ApplicationConfig};
export class TodoListApplication extends BootMixin(
ServiceMixin(RepositoryMixin(RestApplication)),
) {
constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) {
super(options);
// Set up the custom sequence
this.sequence(MySequence);
// ...
}
}
The middleware-based sequence itself is basically a named middleware chain. Each
middleware serves as an action within the sequence. The handle function
executes registered middleware in cascading fashion.
/**
* A sequence implementation using middleware chains
*/
export class MiddlewareSequence implements SequenceHandler {
static defaultOptions: InvokeMiddlewareOptions = {
chain: 'middlewareChain.rest',
orderedGroups: [
// Please note that middleware is cascading. The `sendResponse` is
// added first to invoke downstream middleware to get the result or
// catch errors so that it can produce the http response.
'sendResponse',
// default
'cors',
'apiSpec',
// default
'middleware',
// rest
'findRoute',
// authentication
'authentication',
// rest
'parseParams',
'invokeMethod',
],
};
/**
* Constructor: Injects `InvokeMiddleware` and `InvokeMiddlewareOptions`
*
* @param invokeMiddleware - invoker for registered middleware in a chain.
* To be injected via SequenceActions.INVOKE_MIDDLEWARE.
*/
constructor(
@inject(SequenceActions.INVOKE_MIDDLEWARE)
readonly invokeMiddleware: InvokeMiddleware,
@config()
readonly options: InvokeMiddlewareOptions = MiddlewareSequence.defaultOptions,
) {}
/**
* Runs the default sequence. Given a handler context (request and response),
* running the sequence will produce a response or an error.
*
* @param context - The request context: HTTP request and response objects,
* per-request IoC container and more.
*/
async handle(context: RequestContext): Promise<void> {
debug(
'Invoking middleware chain %s with groups %s',
this.options.chain,
this.options.orderedGroups,
);
await this.invokeMiddleware(context, this.options);
}
}
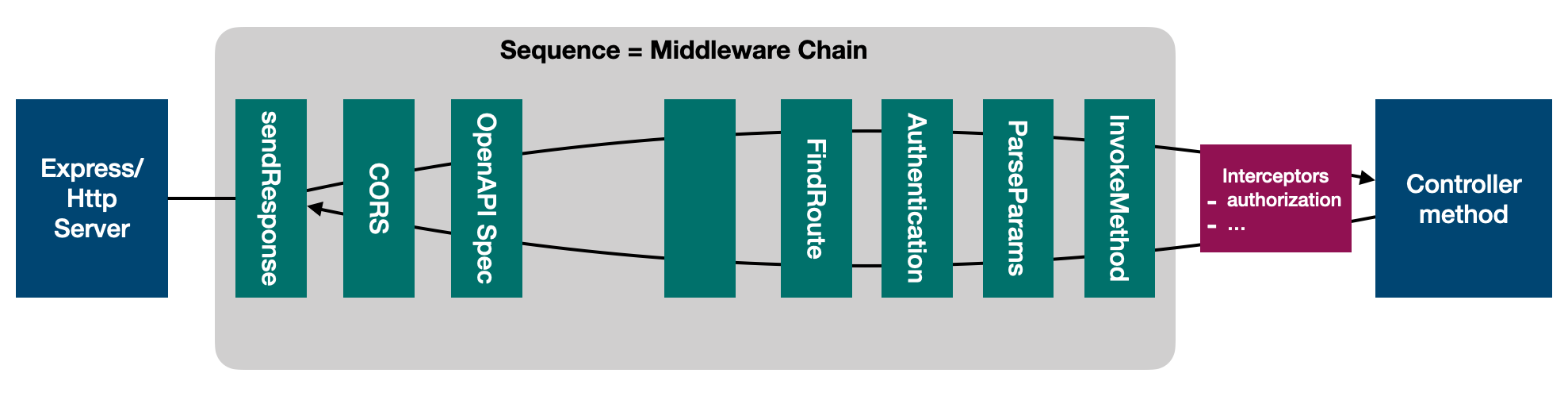
Middleware as actions
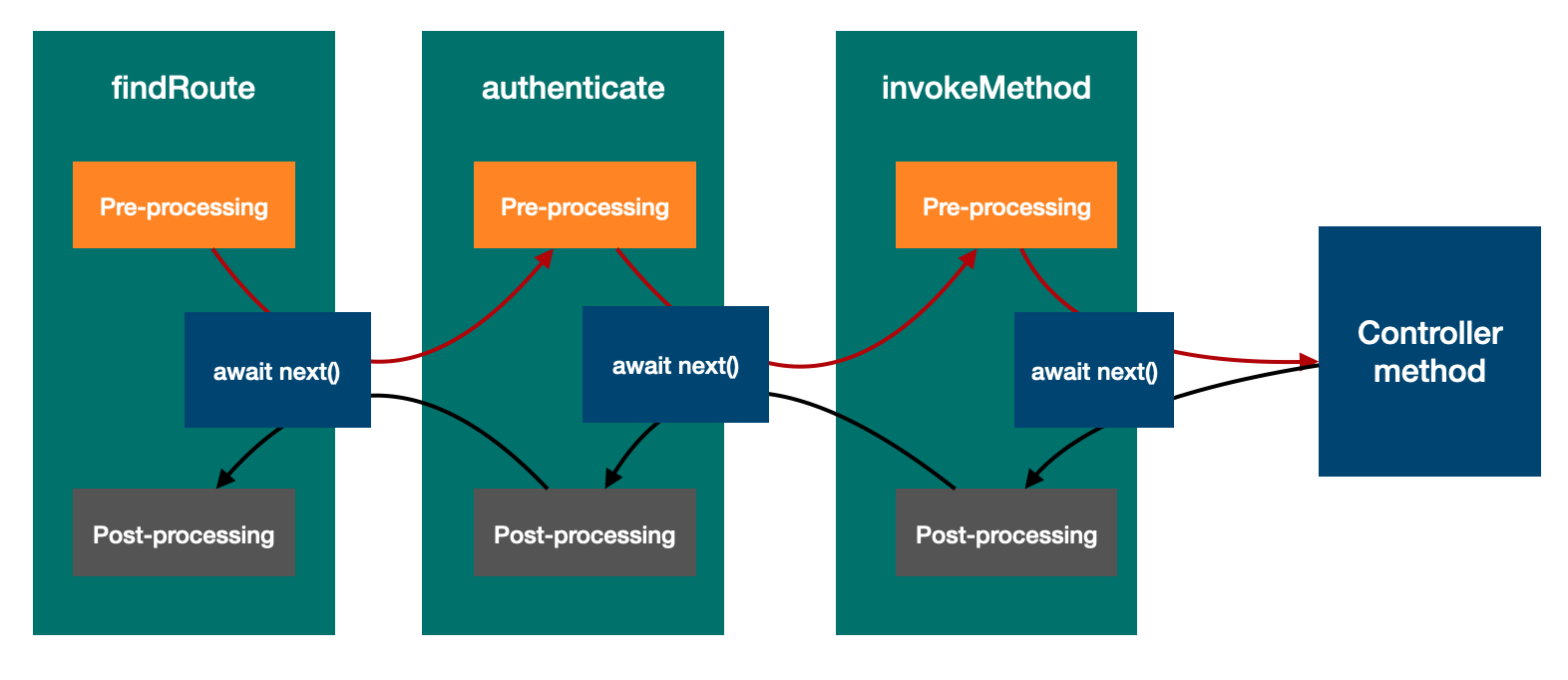
The middleware function is responsible for processing HTTP requests and responses. It typically includes the following logic.
- Process the request from the server or upstream middleware with one of the
following outcomes:
-
Reject the request by throwing an error if the request is invalid
import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { // validate input throw new Error('invalid input'); }; -
Produce a response by itself, such as from the cache
import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { // Find the response from cache const cachedResponse = {}; return cachedResponse; }; -
Proceed by calling
await next()to invoke downstream middleware. Whenawait next()returns, it goes to step 2. If an error thrown fromawait next(), step 3 handles the error.import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { const result = await next(); return result; };
-
- Process the response from downstream middleware or the target operation with
one the following outcomes:
-
Reject the response by throwing an error
import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { const result = await next(); // validate result throw new Error('...'); }; -
Transform the response to a different value
import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { const result = await next(); return {data: result}; }; -
Return the response to upstream middleware
import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { const result = await next(); return result; };
-
-
Catch the error thrown from
await next(). If thecatchblock does not exist, the error will be bubbled up to upstream middleware.import {Middleware} from '@loopback/rest'; const middleware = async (ctx, next) => { try { const result = await next(); return result; } catch (err) { // handle err // either return a new value or throw an error throw err; } };
Default sequence executes these groups of middleware in order:
cors: EnforcesCORSopenApiSpec: Serves OpenAPI specsfindRoute: Finds the appropriate controller method, swagger spec and args for invocationparseParams: Parses HTTP request to get API argument listinvokeMethod: Invokes the API which is defined in the Application controller method
In front of the groups above, we have a special middleware called
sendResponse, which first invokes downstream middleware to get a result and
handles the result or error respectively.
- Writes the result from API into the HTTP response (if the HTTP response has not been produced yet by the middleware chain.
- Catches error logs it using ‘logError’ if any of the above steps in the sequence fails with an error.
Extend the middleware sequence
The middleware based sequence is a middleware chain that accepts contribution of
middleware against RestTags.REST_MIDDLEWARE_CHAIN.
Add middleware to the chain
LoopBack middleware (including Express middleware) can be added to the sequence. See Middleware for more details.
Sort middleware by groups
The middleware for the sequence are executed in the order of groups in a cascading style. The order of groups is determined by two factors:
- The relative order specified for a middleware binding.
-
upstreamGroups: An array of group names that should be upstream to this middleware
@injectable( asMiddleware({ chain: RestTags.REST_MIDDLEWARE_CHAIN, group: 'authentication', upstreamGroups: ['cors', 'findRoute'], }), ) export class AuthenticationMiddlewareProvider implements Provider<Middleware> {} -
downstreamGroups: An array of group names that should be downstream to this middleware
@injectable( asMiddleware({ group: 'sendResponse', downstreamGroups: ['cors', 'invokeMethod'], chain: RestTags.REST_MIDDLEWARE_CHAIN, }), ) export class SendResponseMiddlewareProvider implements Provider<Middleware> {}
-
- The overall order of groups for the sequence
-
It can be set as in
InvokeMiddlewareOptions, which is the configuration for the middleware-based sequence. For example:import {BootMixin} from '@loopback/boot'; import {ApplicationConfig} from '@loopback/core'; import {RepositoryMixin} from '@loopback/repository'; import { InvokeMiddlewareOptions, Request, Response, RestApplication, RestTags, } from '@loopback/rest'; import {RestExplorerComponent} from '@loopback/rest-explorer'; import {ServiceMixin} from '@loopback/service-proxy'; import {MySequence} from './sequence'; export class TodoListApplication extends BootMixin( ServiceMixin(RepositoryMixin(RestApplication)), ) { constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) { super(options); const middlewareOptions: InvokeMiddlewareOptions = { chain: 'middlewareChain.rest', orderedGroups: [ // Please note that middleware is cascading. The `sendResponse` is // added first to invoke downstream middleware to get the result or // catch errors so that it can produce the http response. 'sendResponse', // default 'cors', 'apiSpec', // default 'middleware', // rest 'findRoute', // authentication 'authentication', // rest 'parseParams', 'invokeMethod', ], }; this.configure(RestBindings.SEQUENCE).to(middlewareOptions); // Set up the custom sequence this.sequence(MySequence); } }
When each middleware is added to the chain, its settings of downstreamGroups
and upstreamGroups are honored in conjunction with the overall order. If there
is a conflict, an error will be thrown.
Here are some examples:
- Form a middleware chain with the execution order of
sendResponse => group2 => cors => group1:
orderedGroups: ['sendResponse', 'cors']
middleware 1:
- group: 'group1'
- upstreamGroups: ['cors']
middleware 2:
- group: 'group2'
- downstreamGroups: ['cors']
- a middleware chain with the execution order of
sendResponse => group2 => cors => group1:
orderedGroups: ['sendResponse', 'cors']
middleware 1:
- group: 'group1'
- upstreamGroups: ['group2', 'cors']
middleware 2:
- group: 'group2'
- downstreamGroups: ['cors']
- a middleware chain with an invalid order as
group1andgroup2creates a circular dependency:
orderedGroups: ['sendResponse', 'cors']
middleware 1:
- group: 'group1'
- upstreamGroups: ['group2', 'cors']
middleware 2:
- group: 'group2'
- downstreamGroups: ['group1']
Custom Sequences
Most use cases can be accomplished with MiddlewareSequence. When an app is
generated by the command lb4 app, a sequence file extending
MiddlewareSequence at src/sequence.ts is already generated and bound for you
so that you can easily customize it.
A Sequence class for REST server is required to implement the
SequenceHandler interface:
import {RequestContext} from '@loopback/rest';
/**
* A sequence handler is a class implementing sequence of actions
* required to handle an incoming request.
*/
export interface SequenceHandler {
/**
* Handle the request by running the configured sequence of actions.
*
* @param context - The request context: HTTP request and response objects,
* per-request IoC container and more.
*/
handle(context: RequestContext): Promise<void>;
}
Here is an example where the application logs out a message before and after a request is handled:
import {MiddlewareSequence, Request, Response} from '@loopback/rest';
class MySequence extends MiddlewareSequence {
log(msg: string) {
console.log(msg);
}
async handle(context: RequestContext) {
this.log('before request');
await super.handle(context);
this.log('after request');
}
}
In order for LoopBack to use your custom sequence, you must register it before
starting your Application:
import {RestApplication} from '@loopback/rest';
const app = new RestApplication();
app.sequence(MySequence);
app.start();